The ULT1, ULT2, ULT3 and ULT4-programmes
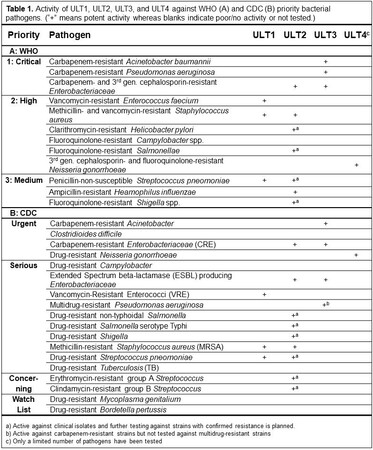
ULT1, ULT2, ULT3, and ULT4 are Ultupharma’s current antibiotics programmes. Antibiotics in these programmes have activity against a wide range of bacterial pathogens in the WHO and CDC priority lists (Table 1, click table to enlarge). A confidential presentation is available describing these programmes.
----------------------------------
ULT1
The ULT1-programme is based on new antibacterial compounds discovered in cultures of Gram-negative soil bacteria, which have shown potent effect against Staphylococcus aureus strains MRSA, MRSE, MSSE, MSSA and VRE and strains resistant to mupirocin, vancomycin, etc. (Bjerketorp et al, J. Nat. Prod., 2017, 80, 2997-3002).
Patents have been granted in Sweden (SE539512) and in the US (US10471043 and US10933048). Several active analogues have been synthesized and more are planned.
----------------------------------
ULT2
Earlier experience from developing antiviral drugs has given a deep knowledge in nucleotide chemistry and biochemistry and resulted in the ULT2-programme containing several treatments active against a large number of multi-resistant Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria such as A. baumannii, E. coli, K. pneumoniae, K. oxytoca, Enterobacter cloacae, E. aerogenes, Serratia marcescens, P. aeruginosa, Proteus mirabilis, Salmonella typhimurium, Shigella sonnei, S. flexneri, Helicobacter pylori, Yersinia pestis, Haemophilus influenza, S. aureus, S. epidermis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Micrococcus luteus, and Bacillus anthracis (Table 2, click table to enlarge).
ULT2A treatments give potent antibacterial effects in mice with peritonitis/sepsis and urinary tract E. coli infections, with no toxicity and at doses expected to be safe in humans. Further development is ongoing, targeting both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacterial infections not responding to treatment with present antibiotics on the market. The therapeutic effects of ULT2 combinations are expected to be more than ten time more potent in humans than in mice as mice have exceptionally high thymidine concentrations counteracting the effect of ULT2 combinations. Humans have very low thymidine levels in blood and urine. ULT2A and ULT2C are likely to inhibit H. pylori at concentrations safe for humans and interesting new possibilities are as cancer prophylaxis and to reduce risk for Alzheimer's and Parkinson's. Another possibility for ULT2A and ULT2C is topical use against several skin infections. This has the advantage of obtaining inhibitory concentrations at the site of infection without effect on the normal bacterial flora at other sites. ULT2C has very potent effect against S. aureus resistant to many antibiotics such as methicillin and mupirosin and resistance to these antibiotics is increasing and a serious problem for patients with diabetic foot infections. ULT2A could also have effect on leishmaniasis as the protozoan causing the disease is inhibited by AZT, which is a component of ULT2A, and the bacteria underlying disease severity are inhibited by ULT2A. The first paper describing ULT2 combinations was recently published in Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy.
Patents have been granted in Sweden (SE540411), the USA (US10828316 and US10828317), Japan (JP6895435), Europe (EP/NL/IE/GB/FR/DE/CH/BE3407898), Hong Kong (HK40000701), China (ZL201780004884.X), Australia (AU2017212224), and Canada (CA3007831).
----------------------------------
ULT3
New ways to isolate bacteria producing novel antibiotic compounds have been developed by Ultupharma in collaboration with the research group at SLU, as described in the recent key-publication in Frontiers in Microbiology: Selective isolation of multidrug-resistant Pedobacter spp., producers of novel antibacterial peptides. One result from these developments is the ULT3-programme, which has a series of bacterial peptides with potent activity against Gram-negative bacteria, including carbapenem-resistant E. coli, A. baumannii and P. aeruginosa, and colistin resistant E. coli, A. baumannii and K. pneumoniae, along with acceptable toxicity and haemolysis properties. These antibiotic peptides are described in a recent publication in ACS Chemical Biology: Isopedopeptins A–H: Cationic Cyclic Lipodepsipeptides from Pedobacter cryoconitis UP508 Targeting WHO Top-Priority Carbapenem-Resistant Bacteria. ULT3 (isopedopeptin B) at sub MIC concentrations can reactivate old antibiotics with resisance problems, indlucing resistance to colistin. A local application of ULT3 in combination with systemic use of old antibiotics offers an interesting possibility to use in surgery.
Patents have been granted in Sweden (SE543054), the USA (US11981759), China (ZL201980056367.6), Japan (JP7492503), Australia (AU2019329130), and national applications are pending in South Korea, Canada and Europe (PCT/SE2019/050789).
----------------------------------
ULT4
The ULT4-programme is the most recent Ultupharma programme, based on new antibacterial alkaloids discovered in fungal cultures. The ULT4 compounds comprise a molecular framework not previously found in any natural product. Synthesis of analogous structures have resulted in compounds with activity against Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Staphylococcus aureus, which are WHO and CDC priority patogens.